Abstract
Aims: Combining 2GTKI+pegylated IFN-a (Peg-IFN) represents an attractive approach for first-line treatment of CP CML, while providing somewhat light additional AEs, it induces high rates of deep molecular responses. We evaluated nilotinib (NIL) alone versus NIL+Peg-IFN in newly diagnosed CP-CML patients (pts) in a randomised phase III trial (PETALs, EudraCT 2013-004974-82) and analysed here the proportion of patients reaching Treatment-Free Remission (TFR) and outcome.
Methods: Newly diagnosed CP CML pts ≤65 years, without vascular history were randomized 1:1 to get NIL 300 mg BID alone [M0 to M72 (unless TFR), arm A] vs Peg-IFN alone for 30 days (M-1→M0) 30 mg/wk, prior to NIL 300 mg BID + Peg-IFN 30 mg/wk 2 wks, upgraded to 45 mg/wk thereafter, for up to 2 y (M0 to M24, arm B) followed by NIL alone until M72 unless TFR. The primary endpoint was the rate of MR4.5 by M12, and after amendment, the trial was extended to 72 months follow-up in order to add, as a secondary endpoint, the TFR rate in pts reaching MR4.5 ≥2 y. The trigger for treatment resumption was loss of MMR. All molecular assessments were centralised until M36, and in case of TFR, MR4.5 was centrally confirmed at M0 TFR, and further molecular follow-up was then performed locally. All molecular quantifications are expressed as BCR-ABL1/ABL1 (IS) in % with ≥32,000 copies of ABL1 as control in the central lab and in the local labs all involved to the pluri-annual French external quality controls. Results are analysed in intention-to-treat.
Results: As previously reported, 200 pts were randomized (99 in A, 101 in B), 130 M and 35 F in each arm, median age of 46 (18-66) y. The median follow-up (FU) since diagnosis is now 47.5 (33.77-62.39) Mo. and the median FU since discontinuation is 9.86 (5.8-23) Mo. in arm A and 15.57 (12.62-22.77) Mo. in arm B. Sokal and ELTS scores were high in 25% and 2.5%, intermediate in 33% and 16.5% and low in 42% and 81% pts respectively, equally balanced. All pts harboured a "Major" BCR transcript. We have previously shown that by M12, the rate of MR4.5 was 15.9% vs 21.5% (primary endpoint met, p=0.049) and that the overall cumulative incidence of MR4.5 was somewhat superior in arm B (54.6 [43.7-65.5] %) vs A (44 [31.5-54] %), p=0.05. Two pts died, one from myeloid blast crisis before TFR (arm A), one from a solid tumour (arm A).
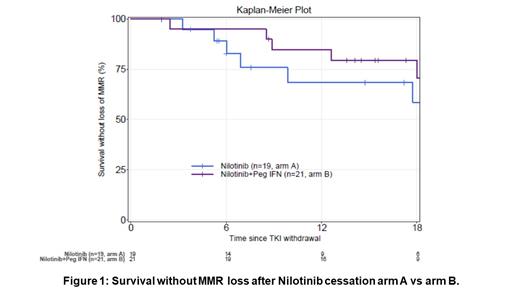
Overall, 40 pts (20%) reached the TFR criteria, 21 in arm A with a median FU of 9.86 (5.8-23) Mo. and 19 in arm B with a median FU since Nilo cessation of 15.57 (12.62-22.77) Mo, partly related to slightly different time for obtaining sustained MR4.5 in favour of arm B (16 vs 13 Mo.). For these 40 pts reaching TFR criteria, there was no statistical difference in terms of age at diagnosis and age at TFR, gender, Sokal, ELTS, FU since diagnosis, undetectability at cessation, BCR-ABL1 levels at 3 Mo. after cessation between the 2 arms. The survival without loss of MMR after cessation is illustrated in Figure 1. It looks superior in arm B over arm A, but did not reach statistical difference (p=0.445), but the FU is very short after cessation yet, especially in arm A.
Once NIL was resumed in the pts that failed TFR, all pts recovered MMR within 6 Mo., with no difference between arms (p=1.00). In univariate analysis, we did not identify significant factor impacting on the TFR success (age at cessation, sex, undetectability at cessation, Sokal, ELTS) except the BCR-ABL1 value at M3-TFR (undetectable versus detectable, HR 7.15 [2.06-24.75], p=0.002), and the duration of MR4.5 before discontinuation (HR 1.11 [1.03-1.19], p=0.004).
During this TFR phase 7 SAEs were reported in arm A (2 pregnancies, 1 obstructive sleep apnea, 1 fever episode, 1 carotid stenosis and 1 femoral stenosis in the same patient at 2 Mo. after cessation, 1 lung carcinoid tumor) and 2 in arm B (1 persistent atrial fibrillation, 1 cholecystectomy).
Conclusions: The combination of NIL + Peg-IFN induces higher MR4.5 rates by M36 in newly diagnosed CP CML pts that may translate in higher successful TFR rates, however a longer follow-up is needed to see consistent significant differences. Updated data will be presented.
Nicolini: Kartos Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding; Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sun Pharma Ltd.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria. Etienne: Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Huguet: Novartis: Other: Advisor; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Advisor; Celgene: Other: Advisor; BMS: Other: Advisor; Amgen: Other: Advisor; Pfizer: Other: Advisor. Guerci-Bresler: Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Charbonnier: Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Rousselot: Incyte, Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding. Deconinck: Stemline Therapetutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Imunogen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Chugai: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Other: Travel Grants, Research Funding; Abbevie: Research Funding. Rea: Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal